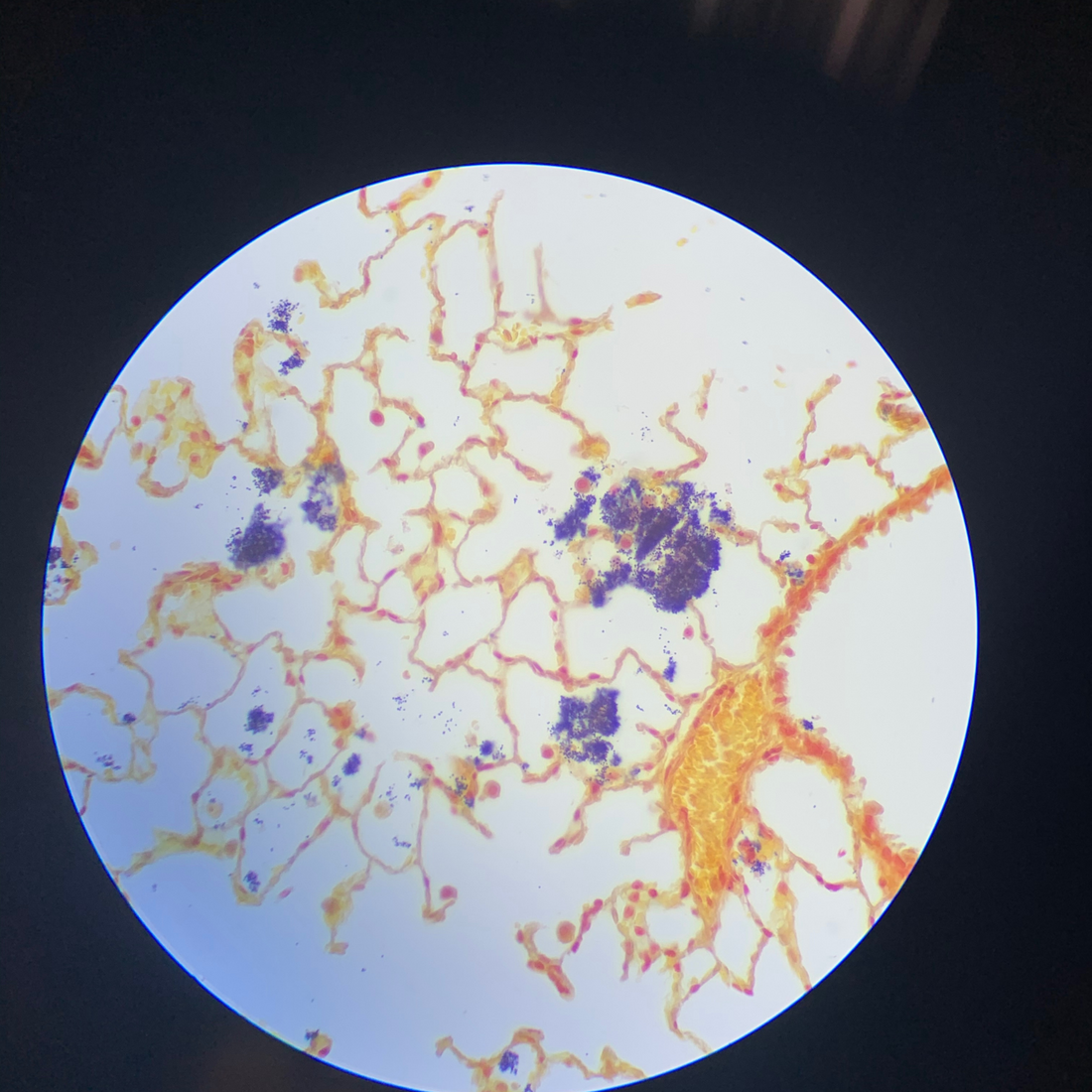
The Gram stain is a staining technique that is used to differentiate and identify bacterial species. It was first developed by Danish bacteriologist Hans Christian Gram in 1884.
Under the microscope, Gram-positive bacteria appear purple, while Gram-negative bacteria appear pink or red.
The Gram stain is a useful tool in the identification and classification of bacterial species, as it allows for the differentiation of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. It is also used to monitor the effectiveness of antibiotic treatments, as some antibiotics are more effective against Gram-positive or Gram-negative bacteria.